VTI is a market-weighted index fund of all the stocks in the United States. It has over $273bn in assets.
SPY is the largest ETF by assets in the world. It seeks to track the performance of the S&P 500.
The main difference between VTI vs SPY is that VTI has exposure to mid and small-cap stocks in the United States. The fees for SPY are also more than double that of VTI.
You can buy partial shares of VTI and SPY at M1 Finance. There’s also other important differences that we’ll cover below.
SPY vs VTI Comparison
The SPDR S&P 500 Trust (SPY) and Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) are both huge index funds.
SPY has $385bn in assets under management while VTI has $273bn.
| VTI | SPY | |
| Assets Under Management | $273bn | $385bn |
| Expense Ratio | 0.04% | 0.0945% |
| Number of Holdings | 4,283 | 508 |
| Inception Date | 5/24/2001 | 1/22/1993 |
| Dividend Yield | 1.28% | 1.32% |
SPY tracks the S&P 500 but holds 508 stocks. VTI has 4,283 holdings because it has all the stocks listed in the United States.
Both funds have been around for over 20 years.
Index Performance Differences
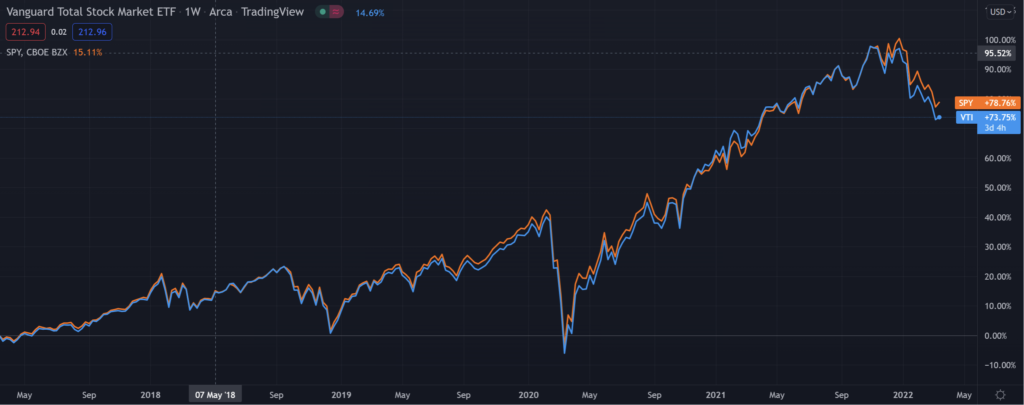
VTI has gone up 6.5%, 60.2% and 92.8% over the past 1, 3 and 5 years.
This compares against SPY which has gone up 10.7%, 63.1% and 96.3% over the past 1,3 and 5 years.
| VTI Performance | SPY Performance | |
| 1 Year Performance | 6.5% | 10.7% |
| 3 Year Performance | 60.2% | 63.1% |
| 5 Year Performance | 92.8% | 96.3% |
The relevant benchmark to compare VTI and SPY to is probably the S&P 500. Over the past 1, 3 and 5 years the S&P 500 has gone up 5.8%, 48.6% and 75.9%.
Fee Differences
The expense ratio for VTI is 0.04%. For SPY, it’s 0.0945%.
That means that if you have $10,000 in VTI you’ll pay $4 a year and for SPY you’ll pay $9.45.
The average expense ratio for equity index funds is 0.58% and the average expense ratio for equity mutual funds is 1.16%.
As some of the biggest index funds in the world, the fees for VTI and SPY are much lower compared to mutual funds and many other index funds and ETFs.
Where Can I Buy VTI Or SPY?
You can buy VTI or SPY at most brokerage accounts. We recommend brokerages that allow you to buy partial shares.
Buying partial shares allows you to dollar cost average the exact amount of money you want to put in rather than buying fewer or more shares than you wanted to because of the high stock price.
M1 Finance is a great choice that is continuing to improve on its already excellent offering.
VTI vs SPY Differences
All the stocks in SPY are included in VTI.
The top 10 holdings of SPY account for 28.3% of the total portfolio. In our cross-holding analysis, for VTI, SPY’s top 10 holdings accounted for 23.9% of the index.
| VTI | SPY | |
| Assets Under Management | $273bn | $385bn |
| Expense Ratio | 0.04% | 0.0945% |
| Number of Holdings | 4,283 | 508 |
| Inception Date | 5/24/2001 | 1/22/1993 |
| Dividend Yield | 1.28% | 1.32% |
In VTI they have a lower weighting because VTI includes smaller stocks listed in the United States.
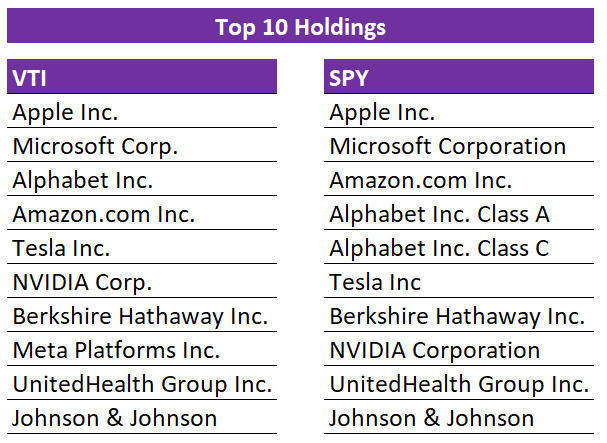
The top 3 holdings of VTI are Apple, Microsoft, and Google.
SPY’s top 3 holdings are Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon.
VTI’s top 3 sectors are Technology, Consumer Discretionary, and Industrials.
The top 3 sectors of SPY are Information Technology, Healthcare, and Consumer Discretionary.
Both ETFs are market weighted. That means that the larger the market cap a company has, the greater its percentage is in the index.
For instance, Apple is worth $2.5 trillion and has a 6.6% weighting in SPY.
Vanguard Total Stock Market Fund (VTI) Overview)
The Vanguard Total Stock Market Fund (VTI) tracks the CRSP US Total Market Index.
CRSP stands for Center for Research in Security Prices. The CRSP US Total Market Index is an index created by a subsidiary of the Chicago Booth School of Business.
To be part of the CRSP index, a stock must be operated for profit, have a stock market value of $15mm+ and have at least 12.5% of its shares trade publicly.
Stocks are added and removed into the index every quarter and IPOs can be in the index a couple of days after they happen.
VTI is offered by Vanguard. Vanguard is a registered investment advisor focused on low-cost index funds with over $7 trillion in assets.
The VTI index fund has $273bn in assets but VTI overall has $1.3 trillion in assets. This is because VTI is an offshoot of Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund Admiral Shares or VTSAX.
The difference between VTI and VTSAX is that VTSAX is a mutual fund that requires that you hold at least $3,000 in the index fund.
If you’re looking for other good Vanguard Funds, VUG is worth taking a look at.
SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) Overview
SPY tracks the S&P 500. It was the first exchange-traded fund listed in the United States and it is managed by State Street Global Advisors.
It’s important to note that State Street doesn’t handle the index inclusion for the S&P 500. Standard and Poors is responsible.
S&P has created the S&P 500 index to track diversified large cap US companies across all 11 GIS sectors.
To be included in the S&P 500, you need to have the following:
- Be based in the US
- Have a market capitaliation of $11.8bn+
- Have a 10% public float
- Be profitable for the last 4 quarters
There’s a lot of discretion with the S&P 500 which we saw when Tesla was added to the index.
Since the SPY and other index funds track the S&P 500, when companies are added or removed from the index, that leads to billions of dollars of buying and selling of stocks included in the index change.
If you’re looking for a higher growth and high risk basket of stocks, you can consider QQQ. We analyzed the differences between QQQ vs SPY here.
What’s Your Pick – VTI or SPY?
We hope our work has given you some insight into the differences between VTI vs SPY.
If you’re looking to invest long-term, dollar cost averaging using partial shares is a solid way to improve your returns.
You can sign up for a brokerage account with these features at M1 Finance.
